Human toxicological risk assessment

What is toxicological risk assessment?
The toxicity of substances used in health and wellness products is a major concern for a company seeking assurance on their quality and safety in use.
Toxicological risk assessment is a qualitative and quantitative process that aims to determine the probability that exposure to one or more exogenous, chemical, physical or biological origin, will produce adverse effects on human health. This risk analysis makes it possible to evaluate products and substances in their context of use by combining different scientific approaches (identification of the danger, risk, weight of proof, PDO, mode of action).
The toxicological risk assessment process is therefore of paramount importance for society as it protects populations exposed to substances contained in food, drugs, consumer products and the environment.
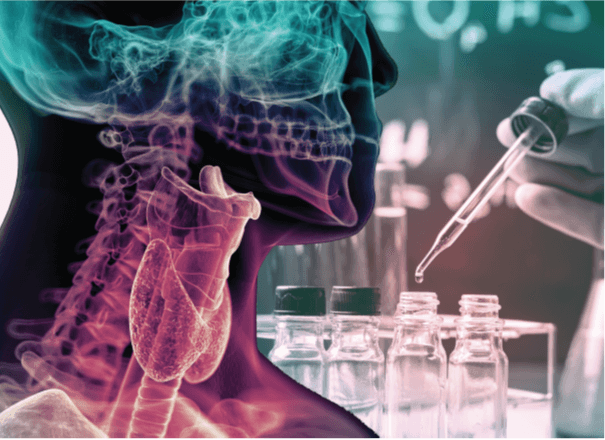
What is endocrine disruption ?
The endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete chemical messengers (hormones) that interact with specific targets (receptors). These interactions lead to the regulation of a wide range of functions including growth, development, reproduction, energy balance, metabolism, and regulation of body weight. The endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands, as well as parts of the kidney, liver, heart, and gonads and can signal each other in series, forming endocrine axes.
The three main endocrine axes are the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonad (HPG) axis, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis. These axes describe the limits within which the endocrine system and endocrine disruption have been confined from the point of view of classical endocrinology. Identifying the intrinsic hazards of substances that may have endocrine properties is a key step in risk management.

What is an endocrine disruptor ?
Endocrine active substances (SASE) are substances which may interact or interfere with normal hormonal activity. When this leads to harmful effects, they are called endocrine disruptors (EDs).
Indeed, according to the definition of the European Union, “an endocrine disruptor is a substance or an exogenous mixture which alters the function (s) of the endocrine system and, consequently, causes harmful effects on health. an intact organism or its progeny or (sub) populations. “
What is nanosafety ?
The nanoforms of some substances may differ from their conventional forms in terms of physicochemical properties, biokinetic behavior and / or biological effects. The uncertainty surrounding the toxicity of nanomaterials therefore deserves specific regulations and assessment approaches.
The particular characteristics identified for nanomaterials and having an impact on safety are mainly size, surface chemistry, charge and shape. On the other hand, classic assessment tools and strategy must be specifically adapted to circumvent experimental issues, adapt conventional metrics and identify and analyze new parameters.
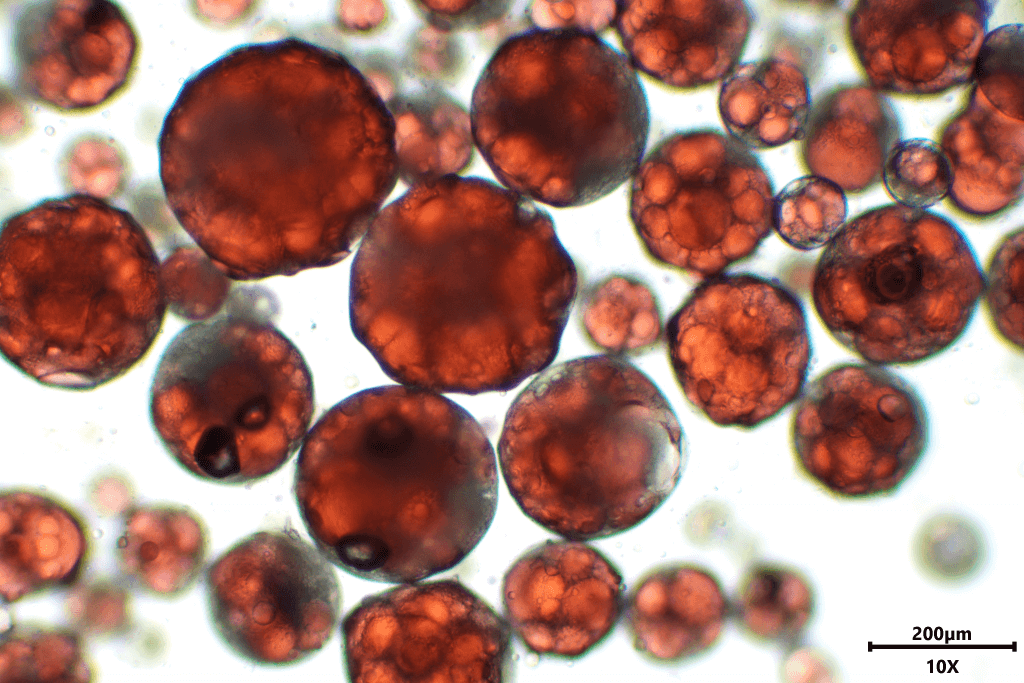
Microencapsulations solutions
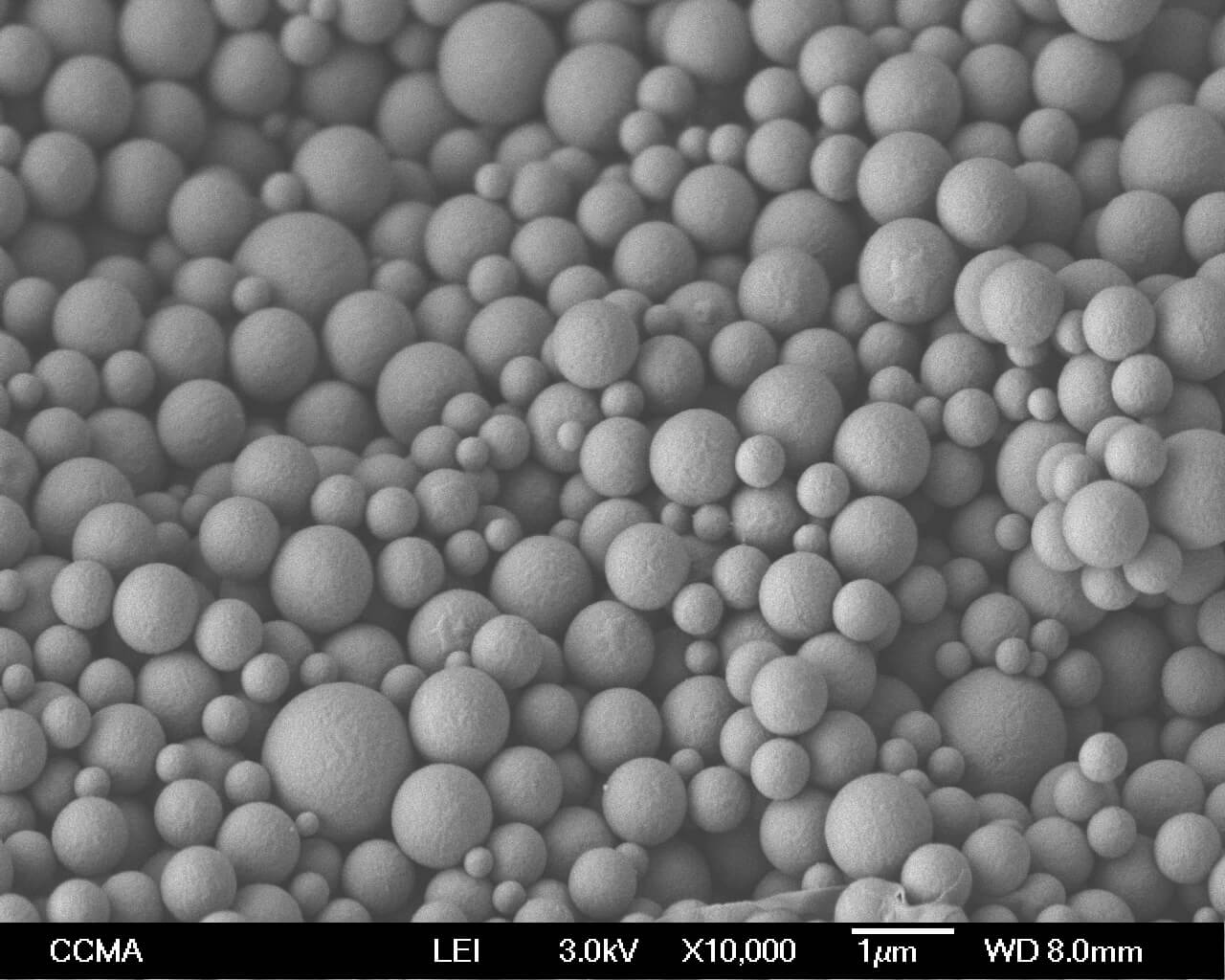

What is microencapsulation?
Microencapsulation is a process that allows a compound or mixture to be incorporated into individual particles of sizes between 1 and 1000 µm. The active can be a solid, liquid or gas. Depending on the technology and the selected encapsulation material, the microparticles can present various morphologies.
Microspheres in which the active is dispersed within the encapsulating material, microcapsules containing a core and a shell, or a combination of both are possible. The objectives sought are mainly to stabilize, protect and control the release of compounds.
What are substainable microencapsulation alternatives to microplastics ?
In the face of increasing pollution from microplastics and their dangers to human health, there is a growing demand from society and regulatory authorities to reduce their use and eliminate “intentionally added microplastics”.
Safer and eco-responsible alternatives to microplastics used for microencapsulation are needed. Numerous alternatives are being developed, notably using polymers, bio-based extracts, and inorganic materials.
What is a biomimicry and how it can applied to responsible innovation?
Biomimicry is an innovation tool that is directly inspired by strategies developed in nature to respond to technical and societal challenges. Biomimicry is one of the solutions used for the development of high-performance products that are part of a sustainable development approach.
What is green chemistry and how its principles can be applied to the development of sustainable microencapsulation technologies?
According to the European Directive 2009/125 / EC, ecodesign is defined as “the integration of environmental characteristics into the design of the product in order to improve the environmental performance of the product throughout its life cycle”.


What is eco-design?
According to the European Environment Agency, eco-design is described as “the integration of environmental aspects into the product development process, by balancing ecological and economic requirements. Eco-design considers environmental aspects at all stages of the product development process, striving for products which make the lowest possible environmental impact throughout the product life cycle”.
